-- Diversion --
Hold my beer meets mass formation psychosis...
Wildebeest from Birdbox Studio
A couple of wildebeest contemplate crossing a river. http://birdboxstudio.com/
www.youtube.com
-- C19 --
Here, apparently, is another bullet in our arsenal against C19 during the pre-hospitalization/outpatient/initial portion of the disease. I have reported on the use D3, C, Zinc, Quercetin, etc. as over-the-counter vitamins/minerals extensively on GITM. Check garyshumway.substack.com for previous issues. And now there's the hormone Melatonin! I believe Dr. Mercola is one of the White Hat docs out there. Taking 1 mg at night about 30 minutes before bed would help with sleep and taking 10 mg if one has the coop appears to be remarkedly effective. Link to the on-line article below with the entire doc reproduced below.
https://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2022/01/13/melatonin-reduces-covid-mortality.aspx
This Hormone May Play a Role on COVID Outcomes.
Optimizing levels of this hormone can lead to better sleep quality, but research suggests it may play a role against viral infections as well. Learn more here.
articles.mercola.com
Melatonin Significantly Reduces COVID-19 Mortality
Analysis by Dr. Joseph Mercola
January 13, 2022
STORY AT-A-GLANCE
While most well-known as a natural sleep regulator, melatonin also has many other important functions. It boosts immune function, helps recharge glutathione and may improve treatment of certain bacterial diseases; it has anticonvulsant and antiexcitotoxic properties, and is a potent antioxidant with the rare ability to enter your mitochondria
In viral infections, melatonin lowers the overreaction of the host cells to the pathogen, thereby raising the host’s tolerance to the virus. This gives the host time to develop the adaptive immune response and eradicate the invading pathogen
Melatonin attenuates several pathological features of COVID-19, including excessive oxidative stress and inflammation, exaggerated immune response resulting in a cytokine storm, acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome
An October 2021 study found melatonin significantly lowered mortality when given to severely infected COVID patients. In the standard care only group, 13 of the 76 patients died (17.1%), compared to just one of the 82 patients (1.2%) who received melatonin in addition to standard care — a reduction in mortality of 93%
During the second week of infection, a time when severely infected patients can take a drastic turn for the worse, the melatonin group fared much better than the standard care only group, with only two patients developing sepsis, compared to eight in the standard care only group
Melatonin is a hormone synthesized in your pineal gland and several other organs,1 indeed in most cells, including human lung monocytes and macrophages, as it is actually synthesized in your mitochondria.2
While most well-known as a natural sleep regulator, melatonin also has many other important functions.3 Notably, it plays an important role in cancer prevention4 and may prevent or improve certain autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes.5
It also has anticonvulsant and antiexcitotoxic properties,6 and is a potent antioxidant7 with the rare ability to enter your mitochondria,8 where it helps prevent mitochondrial impairment, energy failure and the death of mitochondria damaged by oxidation.9 It also:
Boosts immune function
Helps recharge glutathione10 (and glutathione deficiency has been linked to COVID-19 severity)
May improve the treatment of certain bacterial diseases, including tuberculosis11
Helps regulate gene expression via a series of enzymes12
As noted in the Journal of Critical Care:13
“Melatonin is a versatile molecule ... Melatonin plays an important physiologic role in sleep and circadian rhythm regulation, immunoregulation, antioxidant and mitochondrial-protective functions, reproductive control, and regulation of mood. Melatonin has also been reported as effective in combating various bacterial and viral infections.”
Melatonin Also Has Important Role in COVID-19 Treatment
Over the past two years, melatonin has emerged as a surprise weapon against COVID-19. It’s been shown to play a role in viral, bacterial and fungal infections14 and as early as June 2020, researchers suggested it might be an important adjunct to COVID-19 treatment.15,16,17 According to the authors of that paper, melatonin attenuates several pathological features of COVID-19, including:18
Excessive oxidative stress and inflammation
Exaggerated immune response resulting in a cytokine storm
Acute lung injury
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
In October 2020, a scientific review,19 “Melatonin Potentials Against Viral Infections Including COVID-19: Current Evidence and New Findings,” summarized the mechanisms by which melatonin can protect against and ameliorate viral infections such as respiratory syncytial virus, viral hepatitis, viral myocarditis, Ebola, West Nile virus and dengue virus.
Based on these collective findings, they hypothesized melatonin may offer similar protection against SARS-CoV-2. One mechanistic basis for this relates to melatonin’s effects on p21-activated kinases (PAKs), a family of serine and threonine kinases. The authors explain:20
“In the last decade, PAKs have acquired great attention in medicine due to their contribution to a diversity of cellular functions. Among them, PAK1 is considered as a pathogenic enzyme and its unusual activation could be responsible for a broad range of pathologic conditions such as aging, inflammation, malaria, cancers immunopathology, viral infections, etc ...
Interestingly, melatonin exerts a spectrum of important anti-PAK1 properties ... It has been proposed that coronaviruses could trigger CK2/RAS-PAK1-RAF-AP1 signaling pathway via binding to ACE2 receptor.
Although it is not scientifically confirmed as yet, PAK1-inhibitors could theoretically exert as potential agents for the management of a recent outbreak of COVID-19 infection. Indeed, Russel Reiter, a leading pioneer in melatonin research, has recently emphasized that melatonin may be incorporated into the treatment of COVID-19 as an alternative or adjuvant.”
Melatonin Lowers COVID-19 Mortality
Then, on the last day of 2021, Melatonin Research published a research commentary21 discussing an October 2021 study22 by Hasan et. al., which found melatonin significantly lowered mortality when given to severely infected COVID patients. According to the authors:
“In a single-center, open-label, randomized clinical trial, it was observed that melatonin treatment lowered the mortality rate by 93% in severely-infected COVID-19 patients compared with the control group.
This is seemingly the first report to show such a huge mortality reduction in severe COVID-19 infected individuals with a simple treatment. If this observation is confirmed by more rigorous clinical trials, melatonin could become an important weapon to combat this pandemic.”
The commentators point out that, at less than $5 per course of treatment, melatonin is a cost-effective addition to any treatment plan. For comparison, Regeneron monoclonal antibodies cost about $2,100 per dose and remdesivir is $3,100 per treatment. Melatonin also has no serious side effects, so it can be universally used.
In the standard care only group, 13 of the 76 patients died (17.1%), compared to just one of the 82 patients (1.2%) who received melatonin in addition to everything else. That’s a reduction in mortality of 93%.
The Hasan trial23 included 158 hospitalized COVID patients between the ages of 18 and 80. All had confirmed severe SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Eighty-two of the patients were enrolled in the melatonin arm and received 10 milligrams (mg) of melatonin half an hour before bedtime for 14 days, in addition to standard therapeutic care, which included oxygen intubation, remdesivir, levofloxacin (an antibiotic for protection against secondary bacterial infections), dexamethasone (an anti-inflammatory) and enoxaparin (an anticoagulant).
In the standard care only group, 13 of the 76 patients died (17.1%), compared to just one of the 82 patients (1.2%) who received melatonin in addition to everything else. That’s a reduction in mortality of 93%, which is quite remarkable. Three mechanisms of action responsible for this success appears to be a combination of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory activities.24
During the second week of infection, a time when severely infected patients can take a drastic turn for the worse, the melatonin group fared much better than the standard care only group, with only two patients developing sepsis, compared to eight in the standard care only group.25
The Hasan trial also supports findings from a clinical case series26 published in 2020, where patients diagnosed with COVID-19 pneumonia received 36 mg to 72 mg of melatonin intravenously per day, in four divided doses, as an adjunct therapy to standard of care.
All of the patients given melatonin improved within four to five days, and all survived. On average, those given melatonin were discharged from the hospital after 7.3 days, compared to 13 days for those who did not get melatonin.
How Melatonin Prevents Sepsis
This isn’t the first time melatonin has been highlighted for its ability to prevent and treat sepsis. A 2010 paper27 in The Journal of Critical Care noted that melatonin helps prevent and reverse septic shock symptoms by:28
Decreasing synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines
Preventing lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative damage, endotoxemia and metabolic alterations
Suppressing gene expression of the bad form of nitric oxide, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)
Preventing apoptosis (cell death)
Similarly, a 2014 study29 in the Journal of Pineal Research pointed out that melatonin accumulates in mitochondria, and has both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity that could be useful in the treatment of sepsis.
This was a Phase 1 dose escalation study in healthy volunteers to evaluate the tolerability and health effects of melatonin at various dosages. They also assessed the effect of melatonin in an ex vivo whole blood model mimicking sepsis.
No adverse effects were reported for dosages ranging from 20 mg to 100 mg, and the blood model testing revealed melatonin and its metabolite 6-hydroxymelatonin “had beneficial effects on sepsis-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress and cytokine responses …” The authors further explained:30
“Mitochondrial dysfunction initiated by oxidative stress drives inflammation and is generally accepted as playing a major role in sepsis-induced organ failure. It has been recognized that exogenous antioxidants may be useful in sepsis, and more recently, the potential for antioxidants acting specifically in mitochondria has been highlighted.
We showed previously that antioxidants targeted to mitochondria, including melatonin, reduced organ damage in a rat model of sepsis ... In vitro models of sepsis show that melatonin and its major hydroxylated metabolite, 6-hydroxymelatonin, are both effective at reducing the levels of key inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
In rat models of sepsis, melatonin reduces oxidative damage and organ dysfunction and also decreases mortality.
The dose needed for antioxidant action is thought to be considerably higher than that given for modulation of the sleep–wake cycle, but the actual dose required in man is unclear, particularly because the major bioactive effects of oral melatonin in the context of inflammation are likely to be mediated primarily by metabolite levels.”
Melatonin Has Many Mechanisms of Action
When it comes to viral infections, melatonin doesn’t actually target the virus itself. It primarily aids the host, lowering the overreaction of the host cells to the pathogen, thereby raising the host’s tolerance to the virus. As explained in the featured Melatonin Research commentary,31 “This tolerance allows the host sufficient time to develop the adaptive immune response and finally eradicate the invading pathogens.”
By regulating your immune responses, melatonin also helps prevent cytokine storms,32 which is what ultimately kills some patients with serious SARS-CoV-2 infection. Melatonin is also a known cytoprotector with neuroprotective properties that can potentially reduce the neurological sequelae documented in patients infected with COVID-19.33
Part of melatonin’s benefit against COVID may also have to do with the fact that it enhances vitamin D signaling34 and, together, melatonin and vitamin D synergistically enhance your mitochondrial function. In fact, your mitochondria are the final common targets for both.35
I’ve written many articles detailing the importance of vitamin D optimization to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection and more serious COVID-19 illness. The evidence for this is frankly overwhelming, and raising vitamin D levels among the general population may be one of the most important prevention strategies available to us. To learn more, download my vitamin D report, available for free on stopcovidcold.com. Melatonin may also combat SARS-CoV-2 infection by:36
Having an antibacterial effect on white blood cells called neutrophils37 (a high neutrophil count is an indicator for infection)
Suppressing oxidative stress38
Regulating blood pressure (a risk factor for severe COVID-19)
Improving metabolic defects associated with diabetes and insulin resistance (risk factors for severe COVID-19) via inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS)
Protecting mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs, which have been shown to ameliorate severe SARS-CoV-2 infection) against injuries and improving their biological activities
Promoting both cell-mediated and humoral immunity
Promoting synthesis of progenitor cells for macrophages and granulocytes, natural killer (NK) cells and T-helper cells, specifically CD4+ cells
Inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes39 — Inflammasomes are part of your natural immune response. When a pathogen is detected, inflammasomes are activated and start releasing proinflammatory cytokines. The inflammasome NLRP3, specifically, has been identified as a key culprit in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute lung injury, both of which are potential outcomes of COVID-19 infection40
Melatonin Reduces Risk of Positive COVID-19 Test
Data41,42 from Cleveland Clinic also supports the use of melatonin. Here, the researchers analyzed patient data from the Cleveland Clinic’s COVID-19 registry using an artificial intelligence platform designed to identify drugs that may be repurposed.43,44
By identifying clinical manifestations and pathologies shared by COVID-19 and 64 other diseases, they were able to conclude that certain proteins associated with chronic diseases are highly connected with SARS-CoV-2 proteins. Put another way, a number of proteins appear to play a key role in the pathologies seen both in COVID-19 and other chronic diseases.
These connections suggest that drugs already in use for a chronic disease may be repurposed and used in the treatment of COVID-19, as it acts on one or more shared biological targets. Melatonin stood out in this regard. Patients who used melatonin as a supplement had, on average, a 28% lower risk of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2. Blacks who used melatonin were 52% less likely to test positive for the virus.
Unfortunately, two key data points missing from the analysis are the dosage used and the length of supplementation. These data were not included in the patient registry, so we don’t know how much melatonin is required, or how long you need to take it, to lower your risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection to the degree found in this study.
Melatonin Is an Integral Part of Front Line Protocol
Early in 2020, the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC)45 developed preventive, outpatient treatment and inpatient protocols46 based on the insights of the founding critical care doctors. Dr. Paul Marik,47 a critical care doctor known for his life-saving vitamin C sepsis protocol,48 is one of those doctors.
Marik published a paper in the Journal of Thoracic Disease in February 202049 giving the scientific rationale for using melatonin to help regulate the oxidative imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction that are commonly found in sepsis.
This was followed by a paper published in the Frontiers in Medicine in May 2020,50 in which he and a team of scientists presented a therapeutic algorithm for melatonin in the treatment of COVID-19 specifically. “Melatonin's multiple actions as an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antiviral (against other viruses) make it a reasonable choice for use,” they wrote.
Based on its known mechanisms of action, the FLCCC has included melatonin in its early treatment and hospital treatment protocols from the start. You can download the latest protocols on the FLCCC’s website.51
As a supportive therapy, the FLCCC recommends taking 6 mg before bed if you’re treating early or mild symptomatic COVID-19. The hospital treatment protocol calls for anywhere from 6 mg to 12 mg of melatonin at night, until discharge.
For patients treating long-haul COVID-19 syndrome (LHCS), they recommend taking between 2 mg and 12 mg nightly. Begin with a low dose and work your way up as tolerated. If your sleep is disturbed, lower your dose. (Low doses of melatonin will help make you sleepy, while higher doses can trigger sleeplessness.)
General Guidance for Supplementation
While the doses suggested when used against COVID are significantly higher than what you’d normally take to improve your sleep, there does not appear to be any danger to these doses. Research has found no adverse effects for dosages ranging from 20 mg up to 100 mg.52
These dose ranges are up to 100 times more than what a typical conservative dose of 0.5 mg, but it is encouraging that no adverse effects were observed at these high doses. It would still be prudent however to only use doses this high for limited times when you might need them.
Whatever dose you take — and I recommend starting low, at 1 mg or less — be sure to take melatonin at night, before bed. Rising melatonin levels is the reason you feel sleepy in the evening, so it’s ill advised to take it in the morning or during the day, when your natural level is (and should be) low.
Melatonin is also best taken sublingually, either in the form of a spray or sublingual tablet. Sublingually, it can enter your blood stream directly and doesn’t have to go through the digestive tract. As a result, its effect will be felt more rapidly.
Good except why single out health-care workers? Bogus! Gives the camel a nose under the tent and singles out a vocational group to be treated differently. Why are health-care workers subjected to the possible contraindications of the damn jab? Not right! The federal government does not have the constitutional powers to do this. It is a state issue...if that.
https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/courts_law/supreme-court-biden-vaccine-rules/2022/01/13/2e6e4b9e-749e-11ec-bc13-18891499c514_story.html
Supreme Court blocks Biden’s workplace vaccine rules, allows requirement for health-care workers
The administration had argued both policies were needed to push more Americans to get vaccinated against the coronavirus but faced opposition from several Republican-led states and labor groups.
www.washingtonpost.com
Supreme Court blocks Biden’s workplace vaccine rules, allows requirement for health-care workers
Today at 2:49 p.m. EST
The Supreme Court on Thursday stopped the Biden administration’s vaccination-or-testing requirement on the nation’s largest employers, expressing doubt that there is legal authority for such a broad mandate.
But the court allowed a different policy, which requires vaccinations for most health-care workers at the facilities that receive Medicaid and Medicare funds.
Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. and Justice Brett M. Kavanaugh were the only members of the court in the majority of both orders.
Liberal Justices Stephen G. Breyer, Sonia Sotomayor and Elena Kagan would have allowed the workplace requirements. Conservative Justices Clarence Thomas, Samuel A. Alito Jr., Neil M. Gorsuch and Amy Coney Barrett objected to the health-care worker requirements.
The White House said the order covered about 17 million health-care workers, while the requirement on large companies would have covered more than 80 million employees, about two-thirds of the American workforce.
The administration had argued both were needed to push Americans to get vaccinated against covid-19.
Lower courts were split on the ability of federal agencies to impose such requirements. The Supreme Court on Friday held a highly unusual oral argument on the policies, lasting more than three and a half hours.
Businesses and 27 Republican-led states asked the court to put on hold the workplace requirements proposed by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), which had been upheld by a lower court.
The Biden administration asked that the requirements for health-care workers, which courts had put on hold for about half the states, be allowed to move forward.
In weighing previous challenges to coronavirus restrictions and requirements, the court has been largely deferential to state responses to the pandemic — but skeptical of the powers of federal agencies.
That seemed to be the case Friday when court considered the OSHA rule.
Federal law grants OSHA authority to issue emergency rules for up to six months to protect employees “exposed to grave danger” from “substances or agents determined to be toxic or physically harmful or from new hazards.” The administration contends that gives OSHA not only the authority but also the responsibility to act.
The temporary rule would give companies with 100 or more workers a choice: mandate all employees be vaccinated or require unvaccinated employees to provide weekly negative coronavirus test results and wear face coverings to work on-site.
The rules were set to take effect Jan. 4, but OSHA pushed back the date in response to the litigation and said it would not immediately issue citations for those not in compliance.
Soon after the administration announced the rules for private companies in November, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 5th Circuit blocked enforcement of the policy.
But lawsuits emerged around the nation and were consolidated for review by a different court. A panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 6th Circuit dissolved the 5th Circuit’s stay, saying the rules could go into effect.
The other challenged policy was a Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services vaccination requirement for what the White House says is more than 17 million health-care workers at 76,000 facilities that receive federal money tied to those programs.
The administration points to federal law that gives the secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services the ability to impose requirements necessary for the “health and safety” of patients. For decades, it says, the secretary has had authority to require participating health-care providers to establish programs for the prevention and control of infectious diseases within the facilities.
The states challenging the policy said the federal government did not have such coercive powers over the states. As a practical matter, they said, worker opposition to the vaccine would cost the facilities skilled employees at the time they are most needed.
A panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 11th Circuit dismissed a request from Florida to stop the requirement. But a district judge in Missouri stopped the rules, and the 5th Circuit agreed with a challenge from Louisiana.
Because of the uncertainty surrounding the litigation, OSHA announced that it would not penalize companies for not complying with employee testing requirements before Feb. 9, as long as employers show “reasonable, good faith efforts” to meet the standards.
In response to concerns about a shortage of health-care workers, the administration said the secretary of health and human services has given facilities some flexibility to meet the new requirements, including an additional 60 days to get employees fully vaccinated. The agency also said it will hold off on any enforcement action, as long as 90 percent of the workforce is vaccinated and the facility has a plan to immunize its remaining workers.
The OSHA cases are National Federation of Independent Business v. Department of Labor and Ohio v. Department of Labor. The health-care worker cases are Biden v. Missouri and Becerra v. Louisiana.
Ann E. Marimow contributed to this story.
Criminals. Psychotic murders on a Rampage!
https://www.bitchute.com/video/RYALMt8fFytA/
West Australia Almost Entirely Banishes VaxFree From Society Over Experimental Drug Refusal
Join the leading researchers on https://GroupDiscover.com to find the best videos from across the censorship-resistant internet platforms like Odysee, Rumble, LBRY, Bitchute & Brighteon. Add me on these great platforms: https://odysee.com/@TimTru…
www.bitchute.com
-- Politics --
Sen. Sinema is still a D and ignores states rights. But she does make one correct (IMHO) decision. For that, Thank You.
BREAKING: Kyrsten Sinema Kills Democrats' Hopes To Nuke Senate Filibuster After Biden Georgia Speech
Sen. Kyrsten Sinema (D-AZ) says she will not help Democrats nuke the Senate filibuster to pass voting rights legislation, after President Biden urged them to. Stay Connected Forbes on Facebook: http://fb.com/forbes Forbes Video on Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/forbes Forbes Video on Instagram: http://instagram.com/forbes More From Forbes ...
www.youtube.com
https://www.bitchute.com/video/UaAjJdEcCCXN/
33 Million Canadian Devices Monitored, 87% of Canadians Movements SPIED ON!!! THIS Is COVID-19(84)!!
On Parliament Hill, John Brassard, the Conservative critic for ethics and accountable government discussed the Public Health Agency of Canada’s decision to collect data from millions of mobile devices to understand travel patterns during the COVID-1…
www.bitchute.com
https://www.bitchute.com/video/TXaVsMbRHwA/
WHOA! Biden Administration Reroutes $2 Billion In Relief Funds
Recommend skipping over the Hillary hag portion unless you have robust stomach control.
https://www.bitchute.com/video/x8O-N27A4bE/
Watch Kamala Harris' Shocked Face as Host Asks If She Is Being Replaced | DM CLIPS | Rubin Report
Dave Rubin of “The Rubin Report” talks about the rumor that Kamala Harris is going to be replaced. Dave shares a clip of TODAY’s Craig Melvin asking Kamala Harris if the 2024 Democratic ticket will be changing. Kamala gives a shocked reaction when h…
www.bitchute.com
Go to subscribestar and help Dave Cullen. Who's next?
https://www.bitchute.com/video/NOhglEhhBHuM/
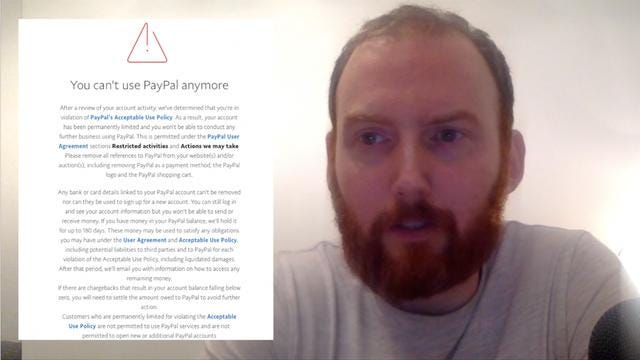
Paypal Have Terminated by Account